Quantum Mechanical Model of Atom
Quantum Mechanical Model of Atom: Overview
This topic presents the important features of the quantum mechanical model of the atom. It explains the relation between the Schrodinger wave equation and the hydrogen atom. We will also learn shape, energies and some rules for the filling of the orbitals.
Important Questions on Quantum Mechanical Model of Atom
A 0.66 kg ball is moving with a speed of 100 m/s. The associated wavelength will be
Which of the following is not permissible arrangement of electrons in an atom?
The measurement of the electron position if associated with an uncertainty in momentum which is equal to . The uncertainty in electron velocity is,
(mass of an electron is )
If uncertainty in position and momentum are equal, then uncertainty in velocity is :
Consider the following sets of quantum numbers :
| (i) | ||||
| (ii) | ||||
| (iii) | ||||
| (iv) | ||||
| (v) |
which of the following sets of quantum number is not possible ?
The orientation of an atomic orbital is governed by
Given : The mass of electron is , Planck constant is the uncertainty involved in the measurement of velocity within a distance of is
The number of orbitals possible for the following quantum numbers is/are
The position of both, an electron and a helium atom is known within . Further, the momentum of the electron is known with in .The minimum uncertainty in the measurement of the momentum of the helium atom is
The position of both, an electron and a helium atom is known within 1.0 nm. Further the momentum of the electron is known within The minimum uncertainty in the measurement of the momentum of the helium atom is
The number of spherical nodes in 3p orbitals are
The electron was shown experimentally to have wave properties by
Calculate the de Broglie wavelength associated with the electron if the velocity of the electron is .
In hydrogen atom, the degeneracy of the level with energy is
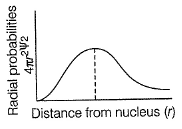
Radial probability density in the occupied orbital of a hydrogen atom in the ground state is given below
What is the difference between probability and radial probability?
What do you mean by radial probability distribution?
Which of the following statements is/are correct?
For radial probability curves, which of the following is/are correct?
The basis of quantum mechanical model of an atom is